In today’s data-driven world, real-time data streaming isn’t just a nice-to-have — it’s essential. Whether it’s a banking app, ride-sharing platform, or recommendation engine, modern applications demand instant, scalable, and reliable data pipelines.
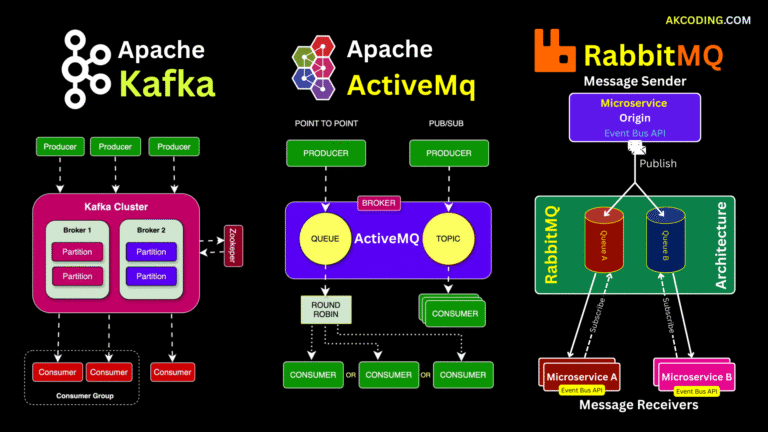
Enter Apache Kafka — the distributed streaming platform trusted by companies like LinkedIn, Netflix, Uber, and Airbnb.
But what exactly is Kafka used for?
Let’s dive into the top 10 real-world use cases of Kafka in modern data architecture.
⚙️ 1. Real-Time Analytics
One of the most common use cases for Kafka is streaming analytics. Companies use it to collect and analyze data as it’s generated — no delays, no batches.
💡 Example: An e-commerce platform tracks live user activity to recommend products on the fly.
🧾 2. Event Sourcing
Kafka shines in event-driven architectures. It stores a sequential log of immutable events, making it easy to rebuild state or audit changes over time.
💡 Example: In a banking system, every transaction is stored as an event, enabling reliable reconciliation and recovery.
🛠️ 3. Log Aggregation
Kafka can unify logs from multiple microservices, servers, or containers, funneling them into a central system for monitoring or debugging.
💡 Example: DevOps teams ingest logs from Kubernetes pods into Kafka and forward them to tools like ELK or Splunk.
🔄 4. Data Integration
Need to move data between MySQL, MongoDB, and Elasticsearch? Kafka works as a central data bus, helping systems communicate reliably at scale.
💡 Example: Kafka Connect syncs data between your production database and a real-time analytics dashboard.
🧠 5. Machine Learning Pipelines
Kafka helps feed ML models with real-time data, enabling live model training, inference, and feedback loops.
💡 Example: A ride-hailing app retrains pricing models based on live demand and traffic data streamed via Kafka.
🧍 6. User Activity Tracking
Track page views, clicks, and interactions as they happen. Kafka helps stream this data for real-time personalization or analytics.
💡 Example: Netflix uses Kafka to capture user events to improve its recommendation engine.
🛡️ 7. Fraud Detection
Real-time anomaly detection is crucial in fintech and e-commerce. Kafka helps detect patterns and trigger alerts within milliseconds.
💡 Example: A bank monitors unusual login locations or transaction spikes using Kafka and stream processing.
📱 8. IoT & Sensor Data Ingestion
IoT devices generate massive volumes of data. Kafka can handle this high-throughput ingestion, even at millions of events per second.
💡 Example: Smart factories stream sensor data to Kafka for predictive maintenance.
📬 9. Asynchronous Messaging (Kafka as a Queue)
Kafka can replace traditional messaging systems (like RabbitMQ) for high-throughput, fault-tolerant communication between services.
💡 Example: A payment service publishes transaction success to Kafka, which is consumed by billing, notifications, and analytics services.
🧩 10. Microservices Communication
Kafka enables loosely coupled microservices to communicate via event streams, reducing tight integrations and improving scalability.
💡 Example: In a food delivery app, order placement, payment, and delivery tracking are decoupled via Kafka topics.

🏁 Final Thoughts
Apache Kafka is no longer just a messaging system — it’s a core part of modern, event-driven, real-time architecture.
Whether you’re building a small-scale application or enterprise-grade platform, Kafka empowers your stack with speed, resilience, and scalability.
🔗 Want to go deeper?
🙌 If you found this helpful:
- 💬 Leave a comment below — What’s your favorite Kafka use case?
- 🔁 Share this post with your dev friends
- 🧠 Follow for more deep dives on data engineering & system design!
Read other awesome articles in Medium.com or in akcoding’s posts.
OR
Join us on YouTube Channel
OR Scan the QR Code to Directly open the Channel 👉