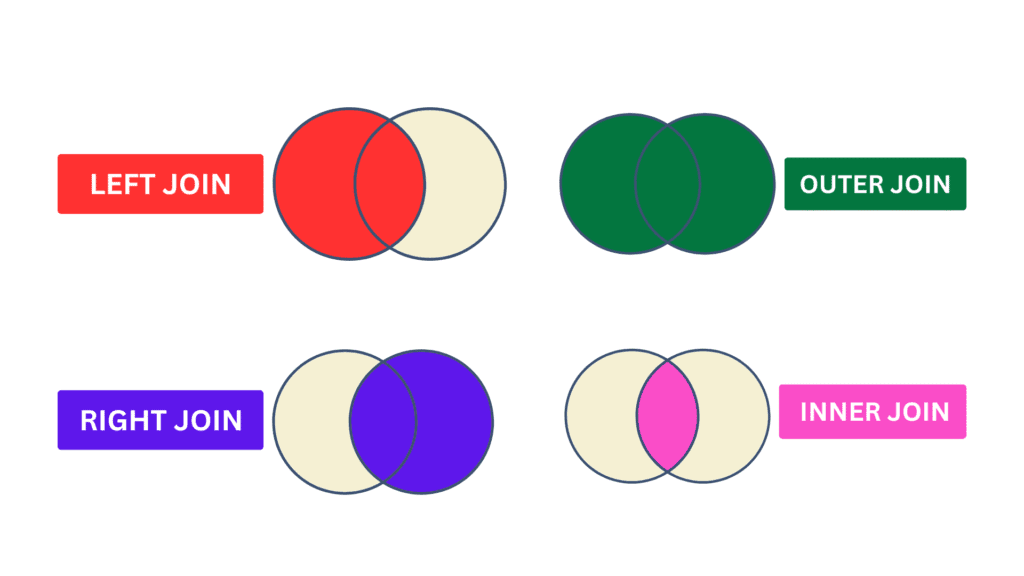
1️⃣ SQL Joins
Used to combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column.
Types of Joins:
- INNER JOIN
→ Returns only matching rows from both tables
Example:
SELECT * FROM orders o
INNER JOIN customers c ON o.customer_id = c.id; - LEFT JOIN (or LEFT OUTER JOIN)
→ All rows from left table + matching rows from right table
→ NULLs for non-matches on the right
Example:
SELECT * FROM customers c
LEFT JOIN orders o ON c.id = o.customer_id; - RIGHT JOIN (or RIGHT OUTER JOIN)
→ All rows from right table + matching rows from left table - FULL JOIN (or FULL OUTER JOIN)
→ All rows from both tables, matching where possible, NULLs otherwise - CROSS JOIN
→ Cartesian product of both tables (every row with every other row) - SELF JOIN
→ Joining a table with itself (useful for hierarchical data)
Performance Tip:
Indexing join columns improves performance.
───────────────────────────────
2️⃣ Subqueries (Nested Queries)
A query within another query, useful for filtering, comparison, and dynamic results.
Types:
- Scalar Subquery: Returns a single value
- Row Subquery: Returns a single row
- Table Subquery: Returns multiple rows/columns
Usage Examples:
- In SELECT clause:
SELECT name, (SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees) AS max_salary FROM department; - In WHERE clause:
SELECT name FROM employees WHERE department_id IN (SELECT id FROM departments WHERE location = ‘NY’); - In FROM clause:
SELECT AVG(salary) FROM (SELECT * FROM employees WHERE department_id = 5) AS sub;
───────────────────────────────
3️⃣ HAVING Clause
Used to filter groups created by GROUP BY.
Difference from WHERE:
- WHERE filters rows before grouping
- HAVING filters groups after aggregation
Example:
SELECT department_id, COUNT()
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id
HAVING COUNT() > 10;
Usage Tip:
Use HAVING only with aggregate functions (COUNT, SUM, AVG, etc.)




