Table of Contents
Below is a clear, minimal-effort, high-impact Technical Roadmap to help you build your own Chargebee-like Billing & Subscription System that can work globally for SaaS products.
This roadmap focuses on MVP essentials, then Phase-2 enhancements, followed by long-term scalable architecture.
Everything is optimized for minimum development effort, maximum usability, and worldwide readiness.
✅ ⚡ MVP Roadmap
MVP = Minimum Viable Product
It means the smallest, simplest version of a product that you can launch quickly
1. Core Components (MUST-HAVE for MVP)
These are the absolute essentials your system needs to start functioning in production.
1️⃣ Customer Management
Minimum Features:
- Create & update customers
- Store email, name, country, and currency
- Customer dashboard (basic)
- Attach payment methods (via Stripe/PayPal API)
Why this matters: every SaaS needs customer identity + payment method storage.
2️⃣ Product Catalog + Plans
Minimum Features:
- Create Products (e.g., CRM, API Access, etc.)
- Create Plans
- Monthly / Yearly
- Price
- Currency
- Support one-time charges
Optional for MVP but good:
- Addons (extra users, storage, etc.)
3️⃣ Subscription Engine (Core Logic)
This is the brain of your billing system.
Minimum Functionality:
- Start subscription
- Cancel subscription
- Pause / Resume subscription
- Change plan (upgrade/downgrade)
- Auto-renew billing cycle
- Trial periods
Key Logic:
- Billing cycle generator
- Proration engine (optional for MVP)
- Invoice generation engine
4️⃣ Payment Processing Integration
For fastest worldwide readiness → integrate:
Option A (single): Stripe Billing API
Option B (multi): Stripe + PayPal
Minimum Requirements:
- Create checkout session
- Handle webhooks
- payment_success
- payment_failed
- subscription_created
- invoice_payment_failed
- Update your DB based on webhook events
5️⃣ Invoicing System (Essential but Lightweight)
Minimum Features:
- Auto-generate invoices (PDF optional, HTML is enough for MVP)
- Store invoice in DB
- Invoice statuses:
- PAID
- UNPAID
- VOID
- UPCOMING
Optional:
- Manual invoice download as PDF
6️⃣ Webhooks & Events System
Needed so that your frontend app knows:
- subscription activated
- payment succeeded
- payment failed
- subscription cancelled
- invoice created
You need:
- Event emitter
- Webhook delivery retry system (at least 3 retries)
7️⃣ Basic Dashboard (Admin UI)
For your internal team:
- Customer list
- Subscription list
- Plan management
- Payment logs
- Event logs
Make it simple, not fancy.
8️⃣ Global SaaS Readiness (Minimum)
- Multi-currency pricing (USD, EUR, GBP, INR at minimum)
- Tax support (basic): add custom GST/VAT %
- Timezone support
- Country-based pricing (optional)
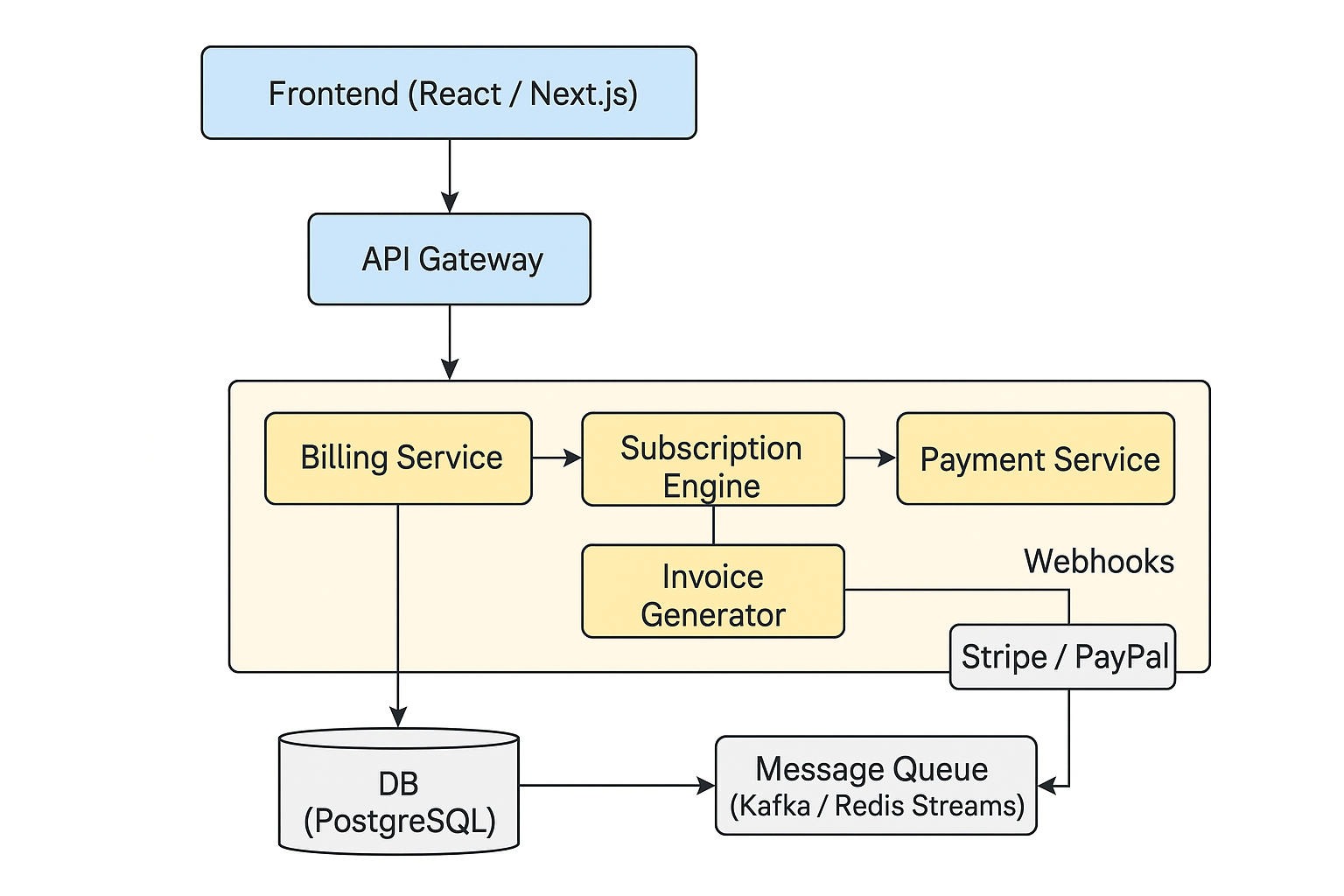
⭐ MVP Architecture
Frontend (React / Next.js)
|
API Gateway
|
Billing Service ---- Subscription Engine
| |
| ----- Invoice Generator
|
Payment Service ---- Stripe/PayPal Integrations
|
Event Service ---- Webhooks
|
DB (PostgreSQL)
|
Message Queue (Kafka/Redis Streams or SQS)
🚀 PHASE-2 FEATURES (After MVP is Live)
1. Advanced Subscription Features
- Usage-based billing
- Metered billing
- Overages
- Seat-based billing
- Multi-tenancy support
- Multiple payment methods
2. Revenue Recovery
- Smart dunning (retry logic)
- Email notifications:
- Payment failed
- Card expiring
- Invoice reminders
3. Tax & Compliance
- Automated GST/VAT via TaxJar
- EU VAT validation
- Multi-country tax rules
4. Analytics Dashboards
- MRR / ARR
- Churn rate
- Active subscribers
- Revenue per plan
5. Integrations
- Webhooks (customer apps)
- Zapier
- Slack
- Salesforce
- HubSpot
🔥 PHASE-3 (Long Term / Enterprise Level)
1. Multi-Gateway Architecture
- Stripe
- Razorpay
- PayPal
- Adyen
- Apple/Google In-app billing
2. PCI-DSS Certification (For card storage)
Only required if you store card details yourself.
Recommended approach: don’t store cards — use Stripe tokens.
3. Ledger System
For finance compliance:
- Immutable ledger
- Double-entry accounting
- Audit reports
4. Marketplace / Multiple Vendors
Like Chargebee Enterprise.
🧱 Minimum Tech Stack Recommendation
| Component | Recommended |
|---|---|
| Backend | Java Spring Boot / Node.js (Fastify/NestJS) |
| Frontend | React / Next.js |
| DB | PostgreSQL (schemas for multi-tenancy) |
| Cache | Redis |
| Queue | Kafka / Redis Streams |
| Payments | Stripe + PayPal |
| Deployment | Kubernetes / ECS |
| Logging | ELK Stack or DataDog |
🎯 MVP Feature Summary for Quick Execution
Minimum Required
- Customer System
- Product & Plans
- Basic Subscription Engine
- Stripe Payments + Webhooks
- Invoice Generator
- Dunning (simple retry)
- Admin Dashboard
- Multi-currency & basic tax
- API for integration
Within 6–8 Weeks Timeline (Small Team)
Yes, this is feasible if scoped properly.
Complete Database Schema
-- Billing System Database Schema (PostgreSQL)
-- Purpose: Minimal-complete schema for a Chargebee-like SaaS billing platform.
-- Notes:
-- * Uses UUID primary keys (pgcrypto/gen_random_uuid())
-- * Uses JSONB for extensible metadata where helpful
-- * Designed for multi-currency, multi-tenant SaaS
-- * Keep proration/usage and ledger primitives for future features
-- Enable UUID function
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS pgcrypto;
-- Tenants (optional, for multi-tenant deployments)
CREATE TABLE tenants (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
name TEXT NOT NULL,
slug TEXT NOT NULL UNIQUE,
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
updated_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now()
);
-- Customers (the buyer)
CREATE TABLE customers (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
external_id TEXT, -- optional mapping to external CRM/legacy ID
email CITEXT NOT NULL,
first_name TEXT,
last_name TEXT,
phone TEXT,
default_currency CHAR(3) DEFAULT 'USD',
default_payment_method_id UUID, -- FK set later to payment_methods
billing_address JSONB,
shipping_address JSONB,
tax_exempt BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE,
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
updated_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
UNIQUE (tenant_id, email)
);
-- Payment methods (tokenized; do NOT store raw PAN)
CREATE TABLE payment_methods (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
customer_id UUID REFERENCES customers(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
provider VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, -- e.g., stripe, paypal
provider_payment_method_id TEXT NOT NULL, -- token/id from provider
type VARCHAR(50), -- card, ach, upi etc
card_brand TEXT,
card_last4 TEXT,
card_exp_month INT,
card_exp_year INT,
billing_details JSONB,
is_default BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE,
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
updated_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now()
);
-- Products (e.g., "CRM Suite")
CREATE TABLE products (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
description TEXT,
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb,
active BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
updated_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now()
);
-- Plans (pricing tiers under products)
CREATE TABLE plans (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
product_id UUID REFERENCES products(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
plan_key TEXT NOT NULL, -- internal key (e.g., "starter_monthly")
name TEXT NOT NULL,
billing_period INTERVAL NOT NULL DEFAULT '1 month', -- 1 month, 1 year
interval_count INT DEFAULT 1,
trial_period_days INT DEFAULT 0,
billing_cycle_anchor TEXT DEFAULT 'start_of_period',
currency CHAR(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'USD',
amount_cents BIGINT NOT NULL, -- amount in smallest currency unit
setup_fee_cents BIGINT DEFAULT 0,
billing_behavior TEXT DEFAULT 'charge_automatically', -- other: send_invoice
active BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE,
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
updated_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
UNIQUE (tenant_id, plan_key)
);
-- Addons (optional extra charges attached to subscriptions)
CREATE TABLE addons (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
description TEXT,
amount_cents BIGINT NOT NULL,
currency CHAR(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'USD',
billing_period INTERVAL,
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb,
active BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
updated_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now()
);
-- Coupons / Discounts
CREATE TABLE coupons (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
code TEXT NOT NULL,
description TEXT,
discount_percent NUMERIC CHECK (discount_percent >= 0 AND discount_percent <= 100),
discount_cents BIGINT, -- fixed amount off (in smallest currency unit)
currency CHAR(3),
duration TEXT DEFAULT 'once', -- once, forever, repeating
duration_in_months INT,
max_redemptions INT,
expires_at TIMESTAMPTZ,
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
updated_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
UNIQUE (tenant_id, code)
);
CREATE TABLE coupon_redemptions (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
coupon_id UUID REFERENCES coupons(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
customer_id UUID REFERENCES customers(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
subscription_id UUID REFERENCES subscriptions(id) ON DELETE SET NULL,
redeemed_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb
);
-- Subscriptions
CREATE TABLE subscriptions (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
customer_id UUID REFERENCES customers(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
plan_id UUID REFERENCES plans(id) ON DELETE SET NULL,
status TEXT NOT NULL DEFAULT 'active', -- active, past_due, canceled, trialing, unpaid
quantity INT DEFAULT 1,
current_period_start TIMESTAMPTZ,
current_period_end TIMESTAMPTZ,
trial_start TIMESTAMPTZ,
trial_end TIMESTAMPTZ,
cancel_at_period_end BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE,
canceled_at TIMESTAMPTZ,
start_date TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
ended_at TIMESTAMPTZ,
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
updated_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now()
);
-- Subscription items (for multiple prices or addons attached to a subscription)
CREATE TABLE subscription_items (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
subscription_id UUID REFERENCES subscriptions(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
plan_id UUID REFERENCES plans(id) ON DELETE SET NULL,
addon_id UUID REFERENCES addons(id) ON DELETE SET NULL,
quantity INT DEFAULT 1,
amount_cents BIGINT NOT NULL,
currency CHAR(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'USD',
billing_period INTERVAL,
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
updated_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now()
);
-- Usage records (for metered billing)
CREATE TABLE usage_records (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
subscription_item_id UUID REFERENCES subscription_items(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
usage_date DATE NOT NULL,
quantity NUMERIC NOT NULL,
description TEXT,
processed BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE,
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now()
);
-- Invoices
CREATE TABLE invoices (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
customer_id UUID REFERENCES customers(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
subscription_id UUID REFERENCES subscriptions(id) ON DELETE SET NULL,
invoice_number TEXT NOT NULL,
status TEXT NOT NULL DEFAULT 'draft', -- draft, open, paid, void, uncollectible
currency CHAR(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'USD',
subtotal_cents BIGINT DEFAULT 0,
tax_cents BIGINT DEFAULT 0,
total_cents BIGINT DEFAULT 0,
amount_due_cents BIGINT DEFAULT 0,
amount_paid_cents BIGINT DEFAULT 0,
due_date TIMESTAMPTZ,
closed_at TIMESTAMPTZ,
pdf_url TEXT,
lines JSONB DEFAULT '[]'::jsonb, -- optional denormalized line items
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
updated_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
UNIQUE (tenant_id, invoice_number)
);
-- Invoice line items (normalized)
CREATE TABLE invoice_items (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
invoice_id UUID REFERENCES invoices(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
subscription_id UUID REFERENCES subscriptions(id) ON DELETE SET NULL,
subscription_item_id UUID REFERENCES subscription_items(id) ON DELETE SET NULL,
description TEXT,
quantity NUMERIC DEFAULT 1,
amount_cents BIGINT NOT NULL,
currency CHAR(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'USD',
period_start TIMESTAMPTZ,
period_end TIMESTAMPTZ,
tax_cents BIGINT DEFAULT 0,
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
updated_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now()
);
-- Payments (records of payments attempted/received)
CREATE TABLE payments (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
customer_id UUID REFERENCES customers(id) ON DELETE SET NULL,
invoice_id UUID REFERENCES invoices(id) ON DELETE SET NULL,
payment_method_id UUID REFERENCES payment_methods(id) ON DELETE SET NULL,
provider VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, -- stripe, paypal
provider_payment_id TEXT,
status TEXT NOT NULL DEFAULT 'processing', -- processing, succeeded, failed, refunded
amount_cents BIGINT NOT NULL,
currency CHAR(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'USD',
captured BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE,
failure_code TEXT,
failure_message TEXT,
refunded_amount_cents BIGINT DEFAULT 0,
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
updated_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now()
);
-- Refunds
CREATE TABLE refunds (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
payment_id UUID REFERENCES payments(id) ON DELETE SET NULL,
provider_refund_id TEXT,
amount_cents BIGINT NOT NULL,
currency CHAR(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'USD',
reason TEXT,
status TEXT DEFAULT 'pending', -- pending, succeeded, failed
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
updated_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now()
);
-- Tax rates (basic support)
CREATE TABLE tax_rates (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
name TEXT,
country CHAR(2),
region TEXT,
rate_percent NUMERIC NOT NULL,
inclusive BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE,
active BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
updated_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now()
);
-- Dunning / Retry attempts
CREATE TABLE payment_attempts (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
invoice_id UUID REFERENCES invoices(id) ON DELETE SET NULL,
payment_method_id UUID REFERENCES payment_methods(id) ON DELETE SET NULL,
attempt_number INT DEFAULT 1,
status TEXT DEFAULT 'failed', -- succeeded, failed
failure_code TEXT,
failure_message TEXT,
next_retry_at TIMESTAMPTZ,
processed_at TIMESTAMPTZ,
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now()
);
-- Events / Webhooks received from payment providers
CREATE TABLE provider_events (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
provider VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
provider_event_id TEXT NOT NULL,
payload JSONB,
processed BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE,
received_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now(),
processed_at TIMESTAMPTZ
);
-- Outgoing webhooks to customer systems
CREATE TABLE outgoing_webhooks (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
target_url TEXT NOT NULL,
event_type TEXT NOT NULL,
payload JSONB NOT NULL,
attempts INT DEFAULT 0,
last_attempt_at TIMESTAMPTZ,
success BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now()
);
-- Ledger (basic immutable ledger for accounting)
CREATE TABLE ledger_entries (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
entry_date DATE NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_DATE,
reference_type TEXT, -- invoice, payment, refund
reference_id UUID,
account TEXT NOT NULL, -- e.g., revenue, receivables
amount_cents BIGINT NOT NULL,
currency CHAR(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'USD',
debit_or_credit TEXT NOT NULL CHECK (debit_or_credit IN ('debit','credit')),
metadata JSONB DEFAULT '{}'::jsonb,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now()
);
-- Audit logs (who did what)
CREATE TABLE audit_logs (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
tenant_id UUID REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
actor_id UUID, -- user/admin id
actor_type TEXT, -- admin, system
action TEXT NOT NULL,
subject_type TEXT,
subject_id UUID,
data JSONB,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now()
);
-- Indexes for performance (examples)
CREATE INDEX idx_customers_tenant_email ON customers(tenant_id, email);
CREATE INDEX idx_subscriptions_customer ON subscriptions(customer_id);
CREATE INDEX idx_invoices_customer_status ON invoices(customer_id, status);
CREATE INDEX idx_payments_invoice_status ON payments(invoice_id, status);
CREATE INDEX idx_usage_records_processed ON usage_records(processed);
-- Triggers to keep updated_at current (simple examples)
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION touch_updated_at()
RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$
BEGIN
NEW.updated_at = now();
RETURN NEW;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
-- Add triggers to a few tables
CREATE TRIGGER touch_customers_updated
BEFORE UPDATE ON customers
FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE PROCEDURE touch_updated_at();
CREATE TRIGGER touch_subscriptions_updated
BEFORE UPDATE ON subscriptions
FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE PROCEDURE touch_updated_at();
CREATE TRIGGER touch_invoices_updated
BEFORE UPDATE ON invoices
FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE PROCEDURE touch_updated_at();
-- Sample sequences / helpers
-- A simple helper to generate readable invoice numbers (tenant-scoped)
CREATE TABLE invoice_counters (
tenant_id UUID PRIMARY KEY REFERENCES tenants(id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
last_serial BIGINT DEFAULT 0
);
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION next_invoice_number(p_tenant_id UUID)
RETURNS TEXT LANGUAGE plpgsql AS $$
DECLARE
s BIGINT;
BEGIN
LOOP
UPDATE invoice_counters SET last_serial = last_serial + 1 WHERE tenant_id = p_tenant_id RETURNING last_serial INTO s;
IF FOUND THEN
RETURN to_char(s, 'FM000000');
END IF;
BEGIN
INSERT INTO invoice_counters (tenant_id, last_serial) VALUES (p_tenant_id, 0);
EXCEPTION WHEN unique_violation THEN
-- concurrent insert, loop and try again
END;
END LOOP;
END;
$$;
-- Example: create a function to reconcile invoice totals (simplified)
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION recompute_invoice_totals(p_invoice_id UUID)
RETURNS VOID LANGUAGE plpgsql AS $$
DECLARE
s_subtotal BIGINT := 0;
s_tax BIGINT := 0;
s_total BIGINT := 0;
s_paid BIGINT := 0;
BEGIN
SELECT COALESCE(SUM(amount_cents),0) INTO s_subtotal FROM invoice_items WHERE invoice_id = p_invoice_id;
SELECT COALESCE(SUM(tax_cents),0) INTO s_tax FROM invoice_items WHERE invoice_id = p_invoice_id;
s_total := s_subtotal + s_tax;
SELECT COALESCE(SUM(amount_cents),0) INTO s_paid FROM payments WHERE invoice_id = p_invoice_id AND status = 'succeeded';
UPDATE invoices SET subtotal_cents = s_subtotal, tax_cents = s_tax, total_cents = s_total, amount_paid_cents = s_paid, amount_due_cents = GREATEST(s_total - s_paid, 0), updated_at = now() WHERE id = p_invoice_id;
END;
$$;
-- End of schema
-- You can extend this schema with: tenant-specific settings, feature flags, advanced tax tables, currency conversion rates, localization tables, and compliance fields (GDPR, consent timestamps).
\Complete System Design Diagram
Security & Compliance
- PCI: do not store card PAN/CVV. Use Stripe Elements or tokenization. If you must store cards (not recommended) — follow PCI-DSS and apply for SAQ/DSS.
- TLS everywhere (mTLS for internal services optional).
- Role-based access control (RBAC) for admin console.
- Secrets: use HashiCorp Vault / cloud KMS.
- Data encryption at rest for DB and object storage.
- Audit logs for all financial operations (immutable where possible).
- GDPR: customer deletion flows — anonymize data with retention windows, keep ledger entries as required by law (mark PII redacted).
Observability & SLOs
Instrumentation:
- Distributed tracing: OpenTelemetry -> Jaeger/Tempo.
- Metrics: Prometheus, Grafana dashboards (MRR, failed payments rate, invoice generation time, queue lag).
- Logs: structured logs to ELK / Datadog / Splunk.
- Alerting: high failure-rate for payments, pod crash loops, DB replication lag, queue consumer lag.
SLO examples:
- Payment success flow end-to-end: 99.9% within 10s (excluding external provider delays).
- Webhook processing: 99.5% within 30s.
- Invoice generation latency: 99% under 2 minutes.
CI/CD & Release strategy
- Git per service (mono-repo optional with clear build pipelines).
- Build → unit tests → integration tests (with test containers for DB) → deploy to staging.
- Canary/Grey deployments with feature flags (LaunchDarkly).
- Blue/Green or Rolling for critical services (Payment Service).
- Migration strategy: use versioned DB migrations (Flyway / Liquibase).
Multi-region & Global considerations
- Localize currency and date/time formatting at UI and invoices.
- For GDPR/EU and local tax: host tenant data in region if requested (data residency) — design by making tenant->region mapping.
- Consider read-replicas in target regions; write region ideally single region per tenant.
- Use CDN for static assets and invoice PDFs.
Developer UX — SDKs & API design
- Provide REST + OpenAPI spec and client SDKs (Node, Java, Python) to increase adoption.
- Design APIs to be intuitive:
POST /v1/subscriptionswithidempotency-keyGET /v1/customers/{id}POST /v1/invoices/{id}/pay
- Provide webhooks docs and test sandbox.
Operational Runbook (short)
- Payment webhook fails: look up provider_event, reconcile payment state, replay events from provider UI.
- Message backlog grows: check consumer lag, scale consumers, inspect slow consumer logs.
- Invoice numbers gap: investigate invoice_counters; use atomic serial function (already in schema).
- Refunds stuck: check provider refund status, reconcile with ledger entries.
Suggested Tech Stack (practical)
- Backend: Java (Spring Boot) or Node.js (NestJS) or Go — choose based on team skill.
- API Gateway: Kong / Nginx / AWS ALB + OIDC provider.
- Messaging: Kafka (high throughput) or Redis Streams (simpler).
- DB: PostgreSQL (per service), Timescale for metrics if needed.
- Cache: Redis.
- Storage: Amazon S3 / MinIO.
- Infra: Kubernetes (EKS/GKE/AKS) or ECS/Fargate.
- Observability: Prometheus + Grafana + Jaeger + ELK.
- CI/CD: GitHub Actions / GitLab CI / Jenkins.
- Payment Providers: Stripe (primary), PayPal / Razorpay / Adyen (regional).
Phased implementation plan (suggested)
Phase 4: Enterprise features (multi-tenant isolation, marketplace).
Phase 0: Infra, CI/CD, API Gateway, Auth Service.
Phase 1 (MVP): Catalog, Customer, Subscription, Payment connector (Stripe), Invoice, minimal Admin UI, Event Bus, Outbox.
Phase 2: Dunning, Usage Metering, Webhook Dispatcher, Ledger, Refunds.
Phase 3: Multi-gateway, tax automation, analytics, multi-region, PCI roadmap if needed.
Below are the major real-world challenges you will face while building and operating a Billing & Subscription Management System (Chargebee-like).
This list includes engineering, business, finance, and compliance challenges — based on how leading billing platforms operate.
🚨 Top Challenges in Building a Billing System
1. Complexity of Subscription Lifecycle
Subscriptions are not just “create and renew.” You must handle:
- Plan changes (upgrade, downgrade)
- Proration (mid-cycle billing)
- Trials, extensions, free credits
- Scheduled changes (future plan switches)
- Pause / resume
- Auto-cancel rules
- Multi-quantity subscriptions
- Metered/usage-based billing
These flows multiply quickly and become challenging to keep consistent and bug-free.
2. Multi-Currency & Global Billing Rules
Billing systems must support worldwide SaaS:
- Different currencies
- Localized invoice formats
- Currency conversion at correct FX rate
- Rounding rules (varies by country)
- Region-specific tax laws (GST, VAT, EU VAT, GST-AU)
Each of these requires domain expertise and continuous updates.
3. Tax Compliance (VAT, GST, Sales Tax)
Tax rules change frequently. Challenges:
- Different tax rates by country/state
- Reverse charge rules
- EU OSS rules
- B2B vs B2C tax differences
- Digital service tax in 40+ countries
- Exemptions and VAT/GST ID validation
- Accurate invoice representation
This is extremely hard to maintain without integrating providers like TaxJar / Avalara.
4. Payment Gateway Variations & Failures
Every payment gateway behaves differently:
- Different APIs (Stripe, Razorpay, PayPal, Adyen)
- Different webhook formats
- Different payment states
- Random downtime
- Card declines for many reasons
- Currency support differences
Ensuring idempotent, fault-tolerant payment processing is a major challenge.
5. Dunning & Payment Recovery Logic
Recovering failed payments is critical for SaaS revenue. Challenges:
- Smart retry strategy
- Handling soft/hard declines
- Timezone-aware retry windows
- Notifications and escalations
- Grace periods
- Suspensions vs cancellations
- Plan downgrade after failure
Bad dunning directly = revenue loss.
6. Handling Usage & Metered Billing at Scale
Usage billing seems simple, but challenges include:
- Billions of usage records
- Duplicate submissions
- Idempotency
- Real-time aggregation
- Backfill & correction
- Delayed reporting
- Large tenants with high throughput
Netflix, AWS, Twilio use extremely complex metering pipelines.
7. Invoice Generation & Numbering
Invoices must be:
- Legally compliant
- Sequentially numbered
- Immutable after finalization
- Localized (PDF, language, currency)
- Accurate tax amounts
- Correct line-item breakdown
A single mistake breaks compliance in many countries.
8. Ledger & Financial Accuracy
A billing system must maintain audit-grade accounting integrity:
- Rigid double-entry ledger
- No negative invoices
- Refund adjustments
- Invoice-credit-note accounting
- FX gain/loss accounting
- Immutable audit logs
This is the hardest part of enterprise-grade billing systems.
9. Multi-Tenancy Challenges
If your system supports multiple SaaS companies:
- Tenant isolation in DB
- Rate limits per tenant
- Custom features per tenant
- Custom taxes/currencies
- Security boundaries
- Global outages affecting all tenants
Most failures come from poor multi-tenancy design.
10. Event Consistency & State Conflicts
Your billing platform depends on async events:
subscription.createdinvoice.generatedpayment.succeededpayment.failed
Challenges:
- Duplicate events
- Out-of-order events
- Lost webhooks
- Race conditions
- Event replay issues
Requires patterns like transactional outbox, idempotency, message versioning.
11. Compliance & Security Requirements
Billing touches financial data; must meet standards:
- PCI-DSS (if storing cards)
- SOC2
- GDPR (data privacy & deletion)
- Data residency (EU, AU, US)
- Secure token storage
- Audit trails
- PII encryption
You must prove that your system is compliant to enterprise buyers.
12. Pricing Experiments & Flexibility
SaaS companies frequently change pricing:
Challenges include:
- Plan versioning
- Grandfathering old customers
- Custom contracts for enterprise clients
- Usage-based pricing variations
- Introductory discounts
- Coupons, promo codes
- Volume-based discounts
Your system must allow these without breaking old subscriptions.
13. Recovering from Webhook Failures
Payment gateways send critical webhooks:
- Payment success
- Payment failure
- Refund processed
- Chargeback initiated
Challenges:
- Retries
- Idempotency
- Out-of-order processing
- Webhook signature verification
- Webhook replay logic
A single missed webhook → incorrect invoice → angry customer.
14. Scaling Events & Batch Jobs
Billing cycles (monthly/weekly/daily) create load spikes:
- Millions of invoices generated at midnight UTC
- Batch payment runs
- Dunning queues
- Usage aggregation windows
Requires distributed schedulers and horizontal scaling.
15. Customer Expectations
Today’s customers demand:
- Instant provisioning
- Real-time dashboards
- Reliable invoices
- Smooth failed payment recovery
- Clear transactional emails
- Integrations with Zapier, Slack, Quickbooks, CRM systems
Meeting all expectations is hard.
16. Global Availability & Latency
If your SaaS is worldwide:
- Users in US, EU, India, Australia need low-latency API access
- Payment providers region-specific
- Data residency rules
- Multi-region failovers
Setting up multi-region architecture is expensive & complex.
17. Maintaining Backward Compatibility
Billing events and APIs cannot be changed easily — customers rely on them.
Challenges:
- Versioning REST APIs
- Versioning events
- Backward compatibility for integrations
- Deprecation timelines
Billing is a core part of revenue — break nothing.
18. Integrations
Billing system must integrate with many external systems:
- CRM (HubSpot, Salesforce)
- Accounting (Quickbooks, Xero)
- Payment gateways
- Tax systems
- Analytics platforms
- Custom internal ERPs
Every integration brings complexity, rate limits, and event-mapping issues.
19. Real-Time Reporting
Customers want dashboards showing:
- MRR / ARR
- Churn
- Expansion revenue
- Cohorts
- Usage consumption
Challenge:
- Large computations
- Real-time updates
- Multi-tenant isolation
- Aggregation from multiple microservices
20. Cost Control & Performance
Billing systems process heavy workloads.
Challenges include:
- Kafka cluster cost
- High DB IOPS
- PDF generation cost
- Caching infrastructure
- Multi-region traffic costs
- Large invoice history storage
Optimize without compromising reliability.
🔥 Final Summary — The Hardest Parts
The top 3 hardest challenges in building a billing system are:
- 1️⃣ Maintaining accurate financial & tax compliance
- 2️⃣ Ensuring payment reliability & dunning
- 3️⃣ Handling complex subscription lifecycle + proration + usage
If you solve these properly, your billing system becomes world-class.
